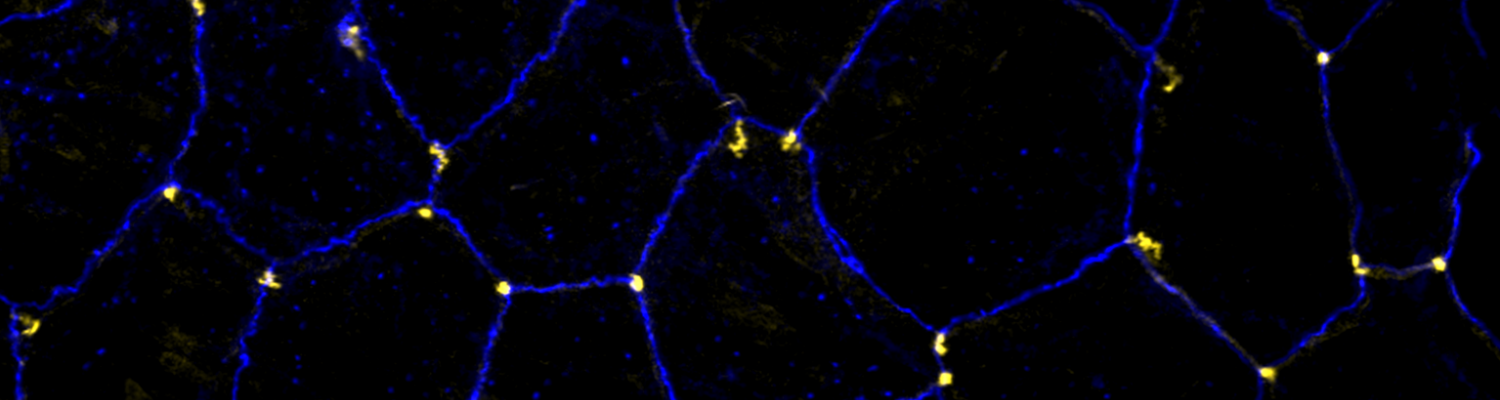
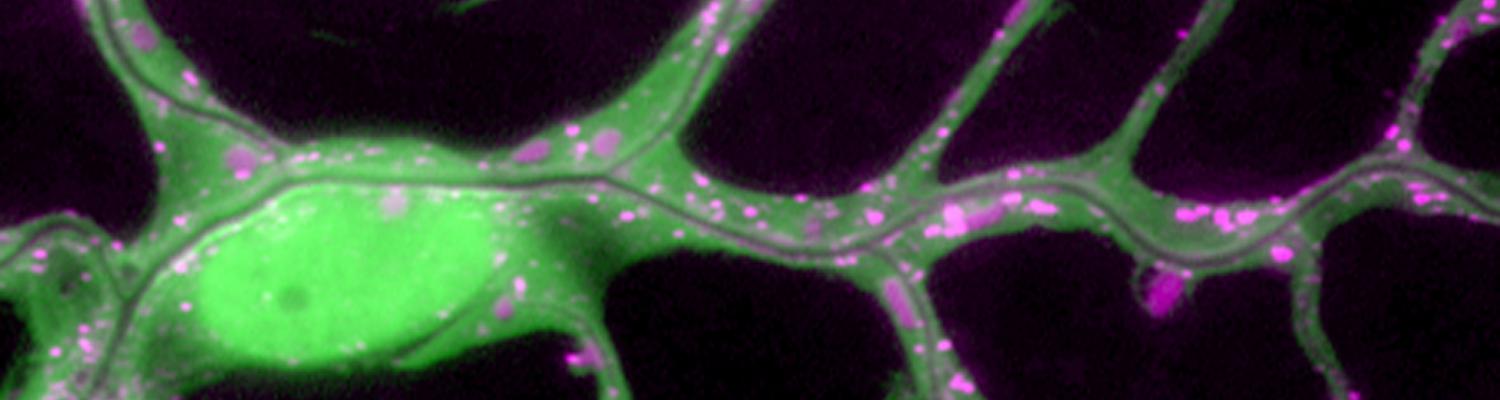
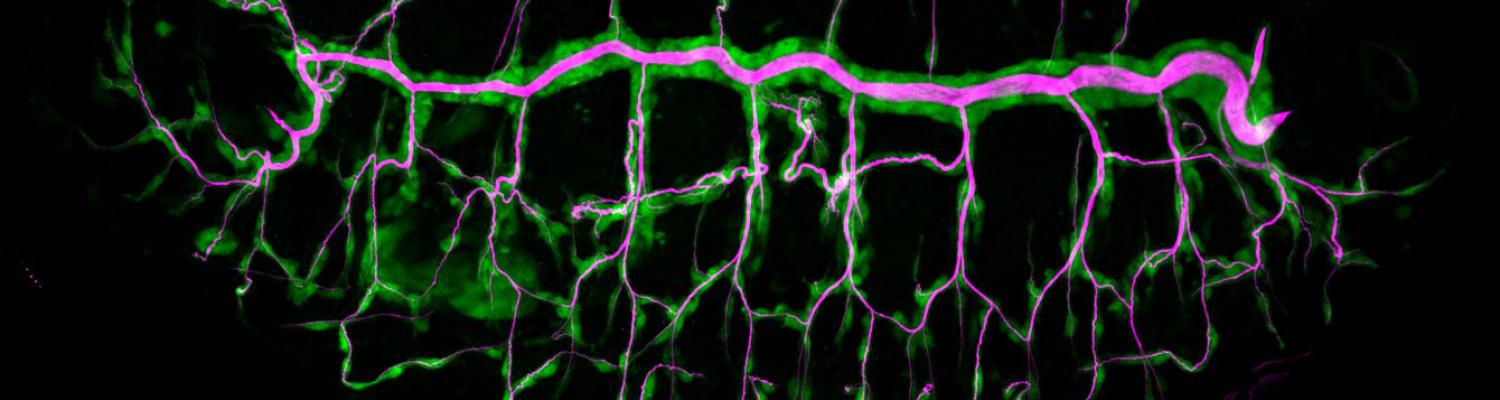
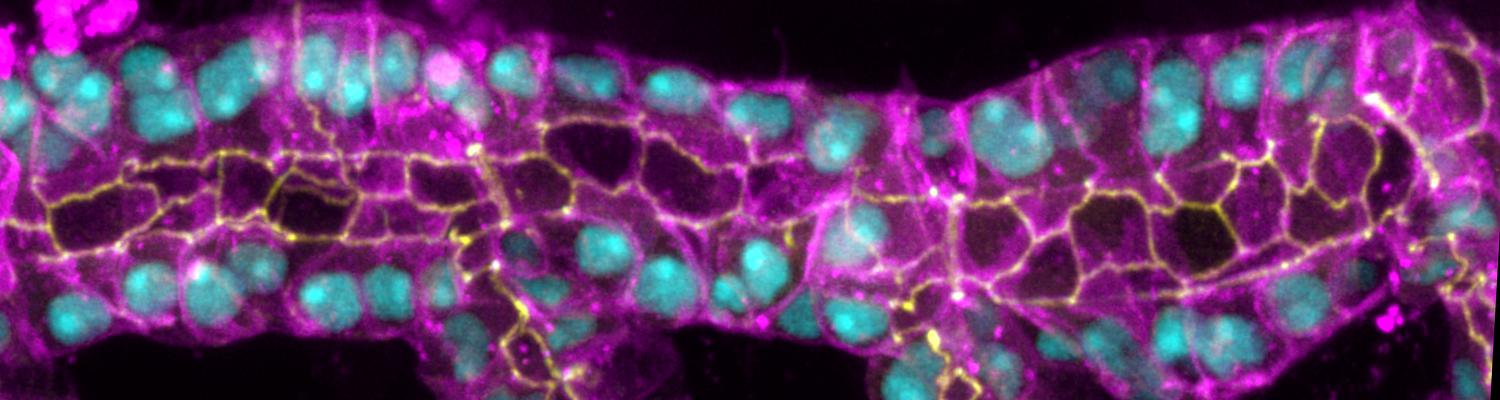
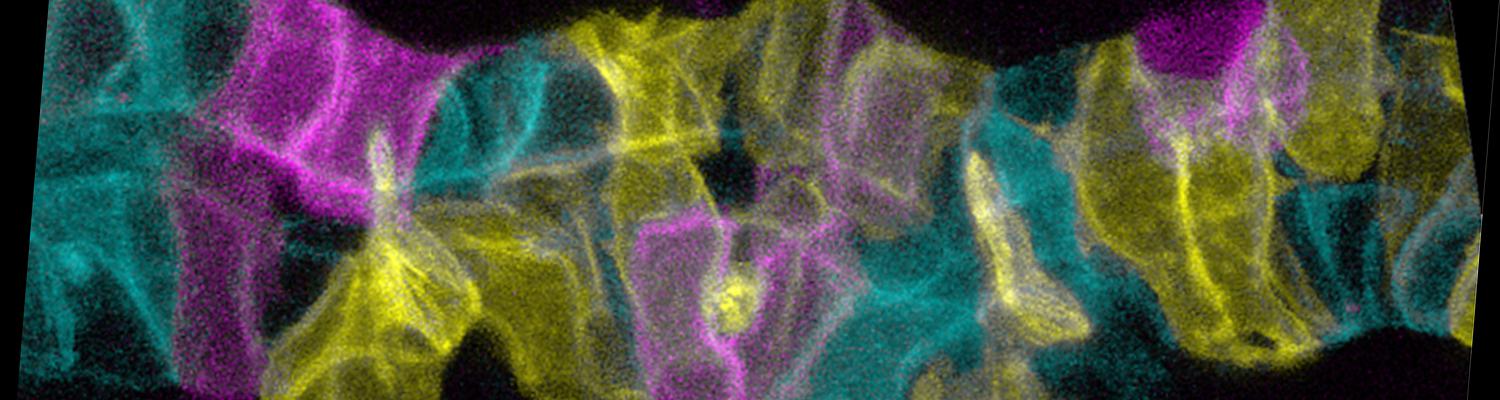
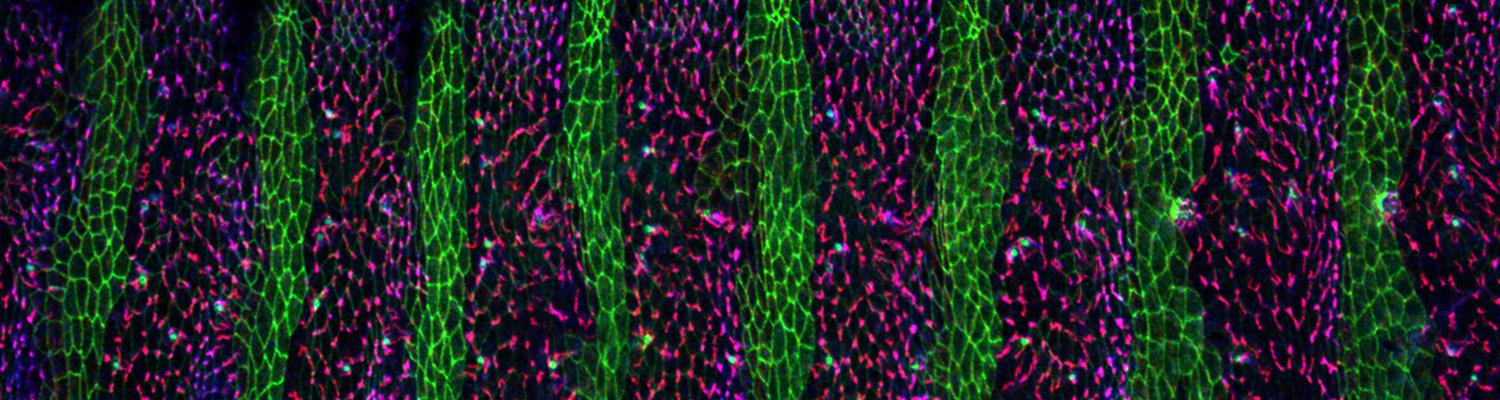
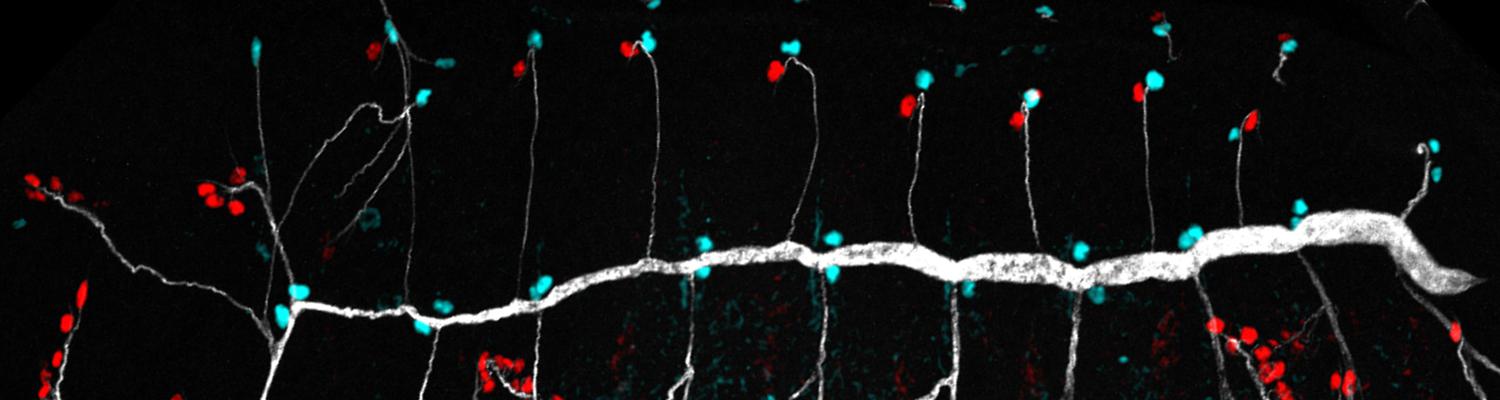
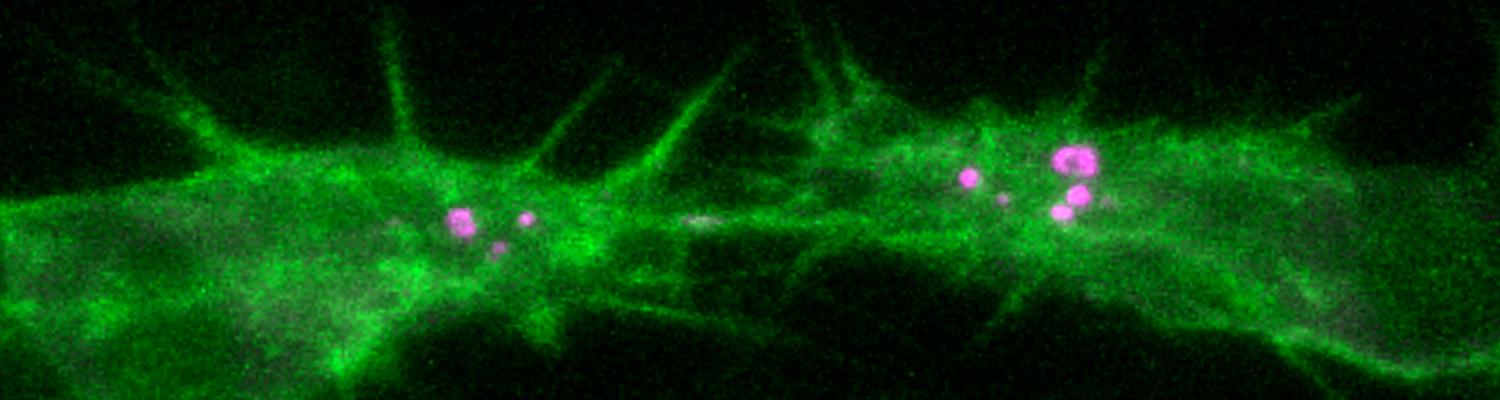
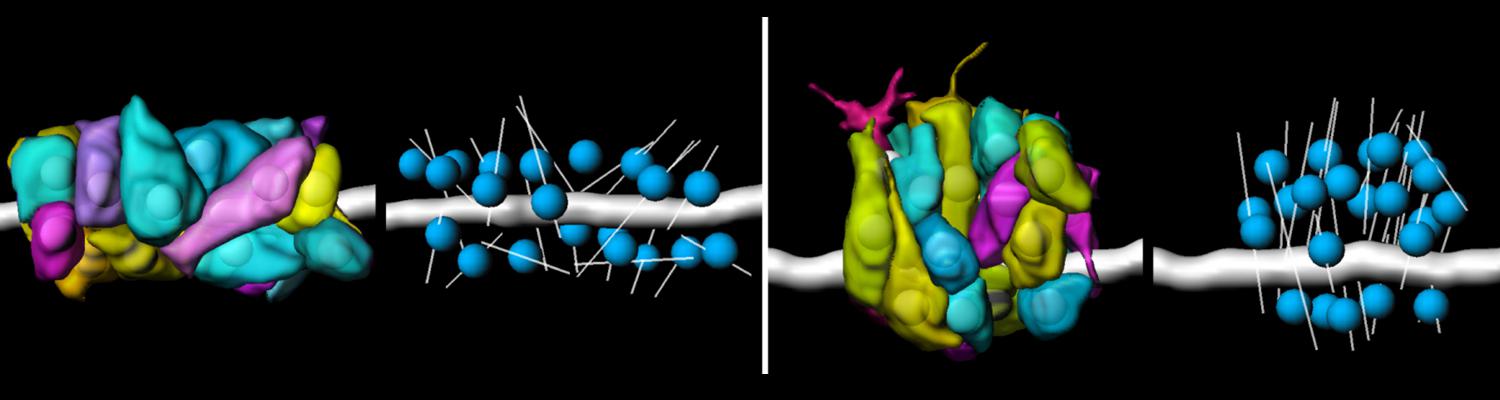
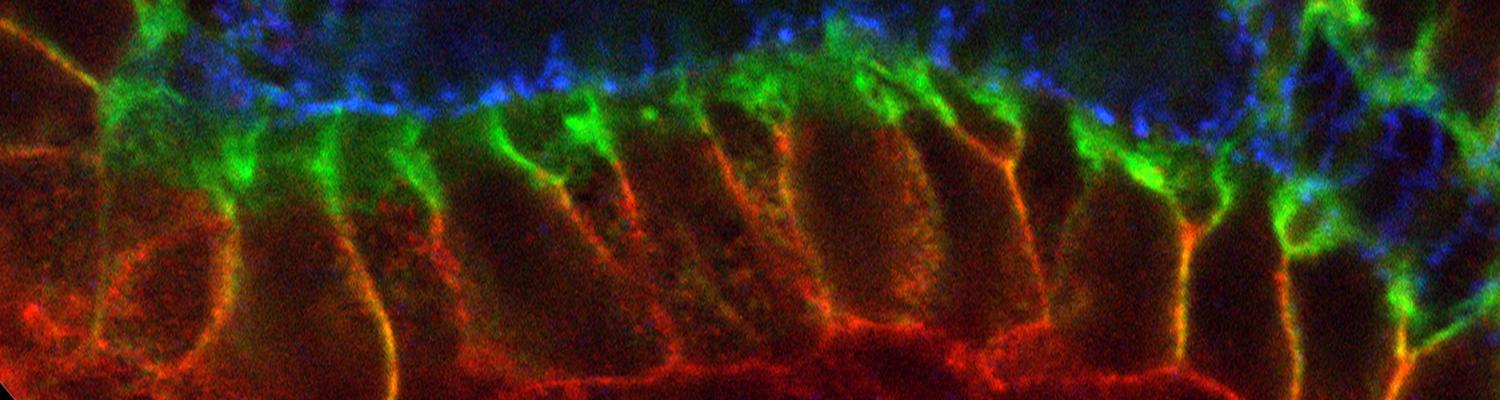
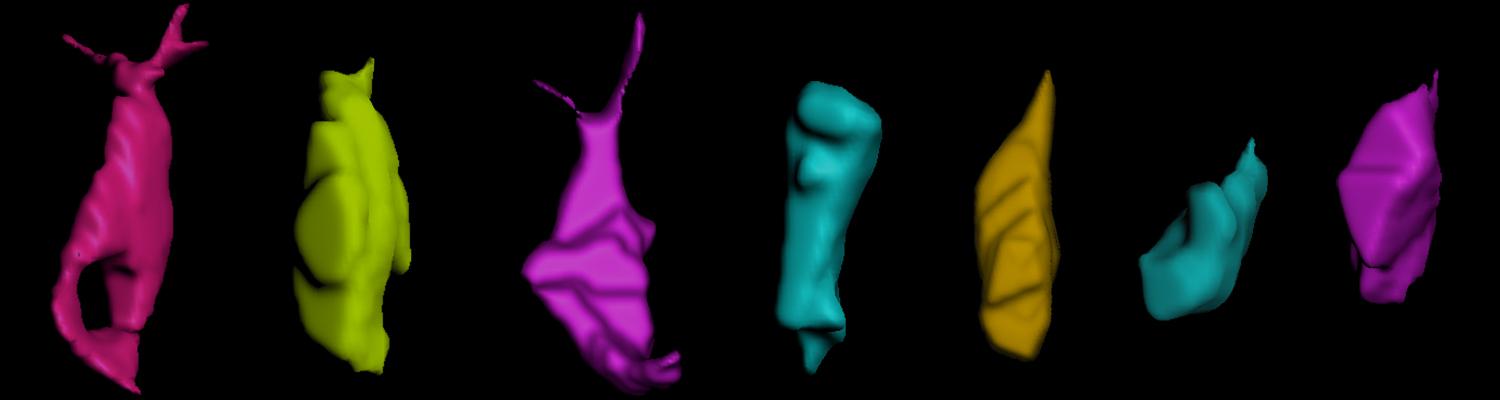
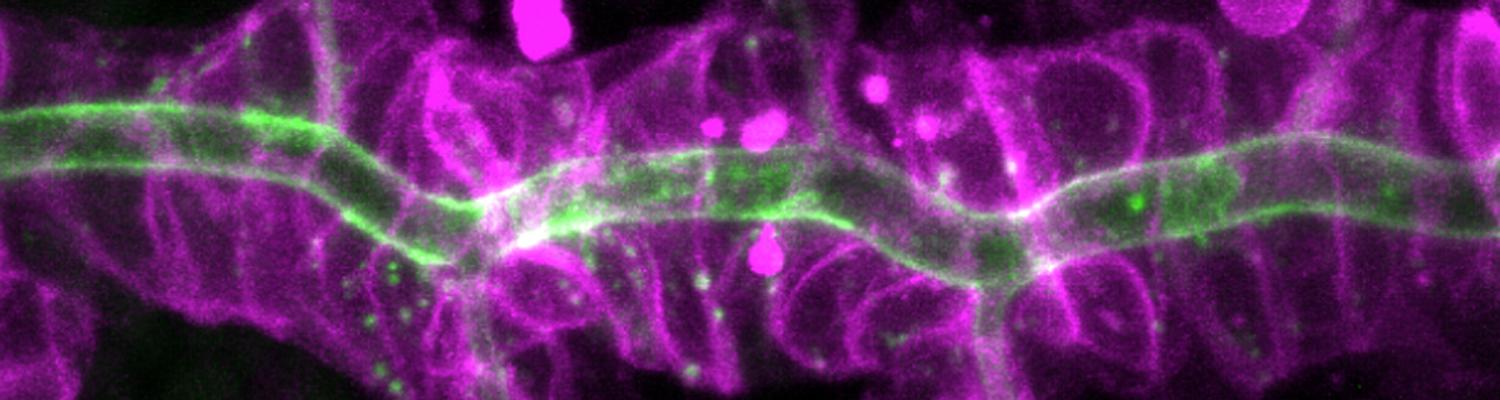
Using the tracheal system in the Drosophila embryo as a model system, we carried out systematic mutagenesis screens, in which we isolated mutations affecting various morphological features (tube length, diameter, luminal shape, tube fusion), as well as cellular processes (secretion, endocytosis, epithelial barrier function). The mutations fall into distinct phenotypic classes, thus providing an entry point towards a comprehensive analysis of the mechanisms underlying tubular morphogensis. New genes are characterized using genetic, cellular, and biochemical approaches. We are focusing on the characterization of genes involved in extracellular matrix deposition during tracheal lumen expansion. We are currently extending the successful screening approach by including more specific readouts for epithelial structure and intracellular trafficking pathways.
Pfadnavigation
- Startseite
- node
- Control of Tracheal Tube Size and Shape
Control of Tracheal Tube Size and Shape
Related Publications
By: Luschnig S, Uv A
Experimental Cell Research | | Volume: 321 | Issue: 1 | 64-70 |Abstract
Tubular epithelia come in various shapes and sizes to accommodate the specific needs for transport, excretion and absorption in multicellular organisms. The intestinal tract, glandular organs and conduits for liquids and gases are all lined by a continuous layer of epithelial cells, which form the boundary of the luminal space. Defects in epithelial architecture and lumen dimensions will impair transport and can lead to serious organ malfunctions. Not surprisingly, multiple cellular and molecular mechanisms contribute to the shape of tubular epithelial structures. One intriguing aspect of epithelial organ formation is the highly coordinate behavior of individual cells as they mold the mature lumen. Here, we focus on recent findings, primarily from Drosophila, demonstrating that informative cues can emanate from the developing organ lumen in the form of solid luminal material. The luminal material is produced by the surrounding epithelium and helps to coordinate changes in shape and arrangement of the very same cells, resulting in correct lumen dimensions.
By: Förster D, Luschnig S
Nature Cell Biology | | Volume: 14 | Issue: 5 | 526-34 |Abstract
Although many organ functions rely on epithelial tubes with correct dimensions, mechanisms underlying tube size control are poorly understood. We analyse the cellular mechanism of tracheal tube elongation in Drosophila, and describe an essential role of the conserved tyrosine kinase Src42A in this process. We show that Src42A is required for polarized cell shape changes and cell rearrangements that mediate tube elongation. In contrast, diametric expansion is controlled by apical secretion independently of Src42A. Constitutive activation of Src42A induces axial cell stretching and tracheal overelongation, indicating that Src42A acts instructively in this process. We propose that Src42A-dependent recycling of E-Cadherin at adherens junctions is limiting for cell shape changes and rearrangements in the axial dimension of the tube. Thus, we define distinct cellular processes that independently control axial and diametric expansion of a cylindrical epithelium in a developing organ. Whereas exocytosis-dependent membrane growth drives circumferential tube expansion, Src42A is required to orient membrane growth in the axial dimension of the tube.
By: Armbruster K, Luschnig S
Journal of Cell Science | | Volume: 125 | Issue: 5 | 1318–28 |Abstract
Protein trafficking through the secretory pathway plays a key role in epithelial organ development and function. The expansion of tracheal tubes in Drosophila depends on trafficking of coatomer protein complex I (COPI)-coated vesicles between the Golgi complex and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). However, it is not clear how this pathway is regulated. Here we describe an essential function of the Sec7 domain guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) gartenzwerg (garz) in epithelial tube morphogenesis and protein secretion. garz is essential for the recruitment of COPI components and for normal Golgi organization. A GFP-Garz fusion protein is distributed in the cytoplasm and accumulates at the cis-Golgi. Localization to the Golgi requires the C-terminal part of Garz. Conversely, blocking the GDP-GTP nucleotide exchange reaction leads to constitutive Golgi localization, suggesting that Garz cycles in a GEF-activity-dependent manner between cytoplasmic and Golgi-membrane-localized pools. The related human ARF-GEF protein GBF1 can substitute for garz function in Drosophila tracheal cells, indicating that the relevant functions of these proteins are conserved. We show that garz interacts genetically with the ARF1 homolog ARF79F and with the ARF1-GAP homolog Gap69C, thus placing garz in a regulatory circuit that controls COPI trafficking in Drosophila. Interestingly, overexpression of garz causes accumulation of secreted proteins in the ER, suggesting that excessive garz activity leads to increased retrograde trafficking. Thus, garz might regulate epithelial tube morphogenesis and secretion by controlling the rate of trafficking of COPI vesicles.
By: Förster D, Armbruster K, Luschnig S
Current Biology | | Volume: 20 | Issue: 1 | 62-68 |Abstract
Epithelial tubes in developing organs, such as mammalian lungs and insect tracheae, need to expand their initially narrow lumina to attain their final, functional dimensions. Despite its critical role for organ function, the cellular mechanism of tube expansion remains unclear. Tracheal tube expansion in Drosophila involves apical secretion and deposition of a luminal matrix, but the mechanistic role of secretion and the nature of forces involved in the process were not previously clear. Here we address the roles of cell-intrinsic and extrinsic processes in tracheal tube expansion. We identify mutations in the sec24 gene stenosis, encoding a cargo-binding subunit of the COPII complex. Via genetic-mosaic analyses, we show that stenosis-dependent secretion drives tube expansion in a cell-autonomous fashion. Strikingly, single cells autonomously adjust both tube diameter and length by implementing a sequence of events including apical membrane growth, cell flattening, and taenidial cuticle formation. Known luminal components are not required for this process. Thus, a cell-intrinsic program, rather than nonautonomous extrinsic cues, controls the dimensions of tracheal tubes. These results indicate a critical role of membrane-associated proteins in the process and imply a mechanism that coordinates autonomous behaviors of individual cells within epithelial structures.
By: Grieder NC, Caussinus E, Parker DS, Cadigan K, Affolter M, Luschnig S
PLoS ONE | | Volume: 3 | Issue: 9 | e3241 |Abstract
BACKGROUND:
There is increasing evidence that tissue-specific modifications of basic cellular functions play an important role in development and disease. To identify the functions of COPI coatomer-mediated membrane trafficking in Drosophila development, we were aiming to create loss-of-function mutations in the gammaCOP gene, which encodes a subunit of the COPI coatomer complex.
PRINCIPAL FINDINGS:
We found that gammaCOP is essential for the viability of the Drosophila embryo. In the absence of zygotic gammaCOP activity, embryos die late in embryogenesis and display pronounced defects in morphogenesis of the embryonic epidermis and of tracheal tubes. The coordinated cell rearrangements and cell shape changes during tracheal tube morphogenesis critically depend on apical secretion of certain proteins. Investigation of tracheal morphogenesis in gammaCOP loss-of-function mutants revealed that several key proteins required for tracheal morphogenesis are not properly secreted into the apical lumen. As a consequence, gammaCOP mutants show defects in cell rearrangements during branch elongation, in tube dilation, as well as in tube fusion. We present genetic evidence that a specific subset of the tracheal defects in gammaCOP mutants is due to the reduced secretion of the Zona Pellucida protein Piopio. Thus, we identified a critical target protein of COPI-dependent secretion in epithelial tube morphogenesis.
CONCLUSIONS/SIGNIFICANCE:
These studies highlight the role of COPI coatomer-mediated vesicle trafficking in both general and tissue-specific secretion in a multicellular organism. Although COPI coatomer is generally required for protein secretion, we show that the phenotypic effect of gammaCOP mutations is surprisingly specific. Importantly, we attribute a distinct aspect of the gammaCOP phenotype to the effect on a specific key target protein.
By: Luschnig S, Bätz T, Armbruster K, Krasnow MA
Current Biology | | Volume: 16 | Issue: 2 | 186-94 |Abstract
Many organs contain epithelial tubes that transport gases or liquids . Proper tube size and shape is crucial for organ function, but the mechanisms controlling tube diameter and length are poorly understood. Recent studies of tracheal (respiratory) tube morphogenesis in Drosophila show that chitin synthesis genes produce an expanding chitin cylinder in the apical (luminal) extracellular matrix (ECM) that coordinates the dilation of the surrounding epithelium . Here, we describe two genes involved in chitin modification, serpentine (serp) and vermiform (verm), mutations in which cause excessively long and tortuous tracheal tubes. The genes encode similar proteins with an LDL-receptor ligand binding motif and chitin binding and deacetylation domains. Both proteins are expressed and secreted during tube expansion and localize throughout the lumen in a chitin-dependent manner. Unlike previously characterized chitin pathway genes, serp and verm are not required for chitin synthesis or secretion but rather for its normal fibrillar structure. The mutations also affect structural properties of another chitinous matrix, epidermal cuticle. Our work demonstrates that chitin and the matrix proteins Serp and Verm limit tube elongation, and it suggests that tube length is controlled independently of diameter by modulating physical properties of the chitin ECM, presumably by N-deacetylation of chitin and conversion to chitosan.
By: Devine WP, Lubarsky B, Shaw K, Luschnig S, Messina L, Krasnow MA
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A | | Volume: 102 | 17014-19 |Abstract
Many organs are composed of branched networks of epithelial tubes that transport vital fluids or gases. The proper size and shape of tubes are crucial for their transport function, but the molecular processes that govern tube size and shape are not well understood. Here we show that three genes required for tracheal tube morphogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster encode proteins involved in the synthesis and accumulation of chitin, a polymer of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosamine that serves as a scaffold in the rigid extracellular matrix of insect cuticle. In all three mutants, developing tracheal tubes bud and extend normally, but the epithelial walls of the tubes do not expand uniformly, and the resultant tubes are grossly misshapen, with constricted and distended regions all along their lengths. The genes are expressed in tracheal cells during the expansion process, and chitin accumulates in the lumen of tubes, forming an expanding cylinder that we propose coordinates the behavior of the surrounding tracheal cells and stabilizes the expanding epithelium. These findings show that chitin regulates epithelial tube morphogenesis, in addition to its classical role protecting mature epithelia.
By: Ghabrial A, Luschnig S, Metzstein MM, Krasnow MA
Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology | | Volume: 19 | 623-47 |Abstract
Many organs including the mammalian lung and vascular system consist of branched tubular networks that transport essential gases or fluids, but the genetic programs that control the development of these complex three-dimensional structures are not well understood. The Drosophila melanogaster tracheal (respiratory) system is a network of interconnected epithelial tubes that transports oxygen and other gases in the body and provides a paradigm of branching morphogenesis. It develops by sequential sprouting of primary, secondary, and terminal branches from an epithelial sac of approximately 80 cells in each body segment of the embryo. Mapping of the cell movements and shape changes during the sprouting process has revealed that distinct mechanisms of epithelial migration and tube formation are used at each stage of branching. Genetic dissection of the process has identified a general program in which a fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) are used repeatedly to control branch budding and outgrowth. At each stage of branching, the mechanisms controlling FGF expression and the downstream signal transduction pathway change, altering the pattern and structure of the branches that form. During terminal branching, FGF expression is regulated by hypoxia, ensuring that tracheal structure matches cellular oxygen need. A branch diversification program operates in parallel to the general budding program: Regional signals locally modify the general program, conferring specific structural features and other properties on individual branches, such as their substrate outgrowth preferences, differences in tube size and shape, and the ability to fuse to other branches to interconnect the network.